Alarm Fatigue in Network Monitoring!!
Imagine a fire alarm constantly blaring, not because of a real fire, but due to a faulty smoke detector. This is the reality for many network operations centers, where a constant barrage of irrelevant alarms drowns out genuine alerts. This “alarm fatigue” not only hampers productivity but also increases the risk of missing critical events. In this blog post, we’ll explore strategies to streamline your network monitoring and reduce alarm fatigue, enabling you to focus on what truly matters.
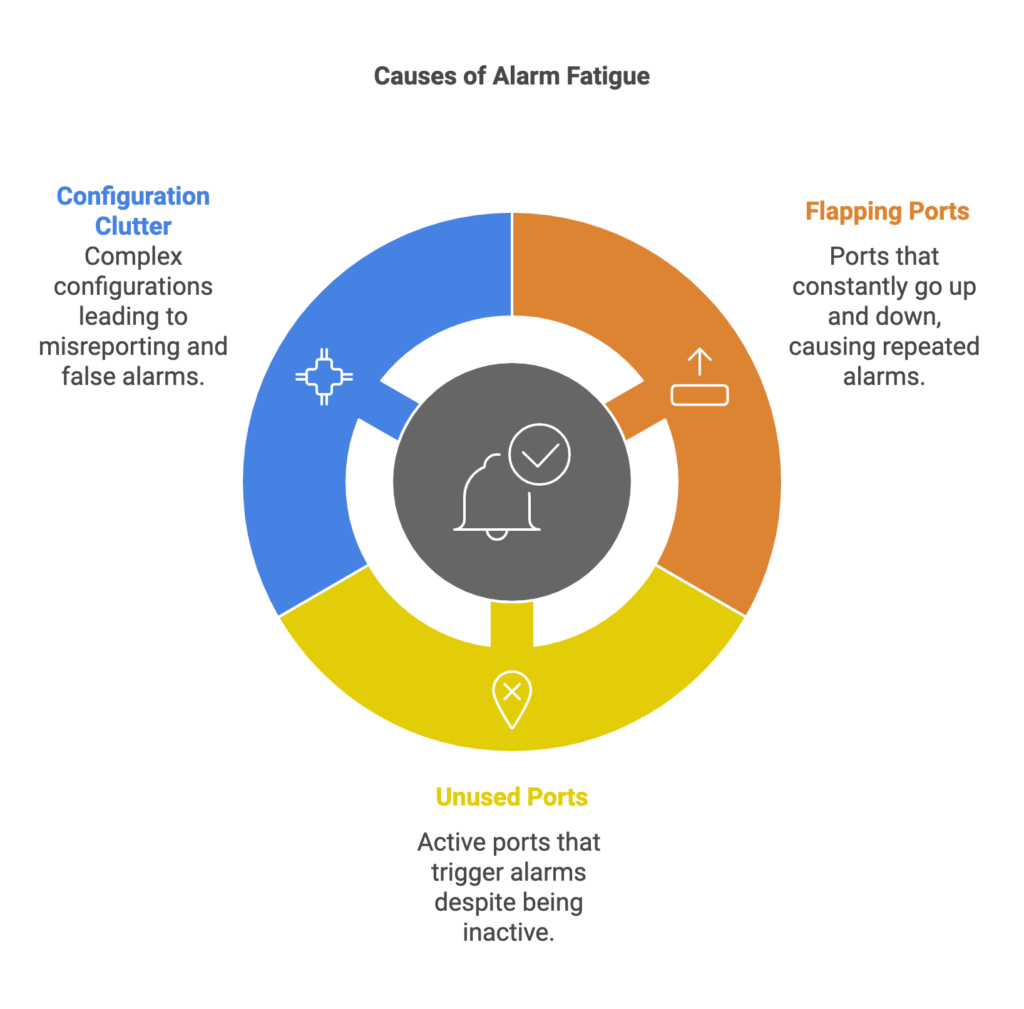
Causes of Alarm Fatigue
Alarm fatigue typically arises from a combination of factors, all of which contribute to the unnecessary escalation of alerts. Some of the most common culprits include:
- Flapping Network Ports
A flapping port occurs when a network port constantly goes up and down, often due to physical issues or misconfigurations. This causes repeated alarms, which can quickly become overwhelming. While a single instance may not be critical, ongoing flapping can generate a flood of alerts, making it difficult to identify other issues. - Unused or Unnecessary Ports
Another major contributor to alarm fatigue is the presence of unused network ports that remain active and monitored. These ports might trigger alarms even though they aren’t actually in use, creating unnecessary noise in your monitoring system. Whether due to legacy configurations or overlooked devices, these dormant ports still contribute to the flood of alerts. - Excessive Configuration Clutter
Overly complex and outdated network configurations can also play a significant role in alarm fatigue. When configurations are not cleaned up or optimized, they can lead to misreporting or the generation of false alarms. Having too many redundant or unnecessary network rules can confuse the system, making it harder to differentiate between meaningful and meaningless alerts.
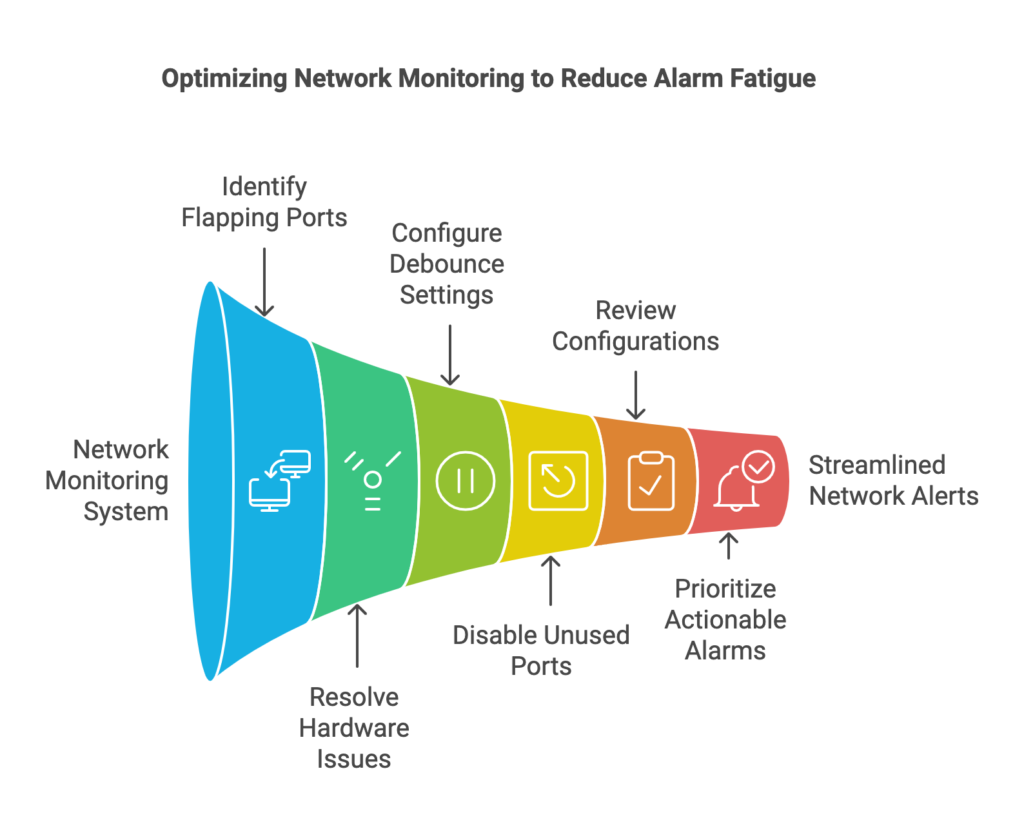
How to Streamline Your Network Monitoring
Now that we’ve identified some of the primary causes of alarm fatigue, let’s look at how to address them and optimize your network monitoring.
1. Address Flapping Ports
One of the first steps in reducing alarm fatigue is to identify and resolve flapping network ports. Tools like NetFlow or SNMP can help you monitor port status and pinpoint when ports are repeatedly going up and down. Once identified, try the following actions:
- Check for hardware issues: Faulty cables or hardware often cause port flapping. Swap out cables or replace defective devices.
- Ensure proper configuration: Misconfigured ports, such as speed mismatches or duplex settings, can lead to flapping. Verify that your network settings are correct.
- Use “debounce” settings: Some network monitoring tools allow you to configure “debounce” thresholds, meaning they will ignore small fluctuations in port status for a specific amount of time. This can help filter out transient issues that don’t need immediate attention.
2. Shut Down Unused Ports
An effective way to reduce unnecessary alerts is by shutting down unused network ports. Ports that are not in use should be disabled or physically disconnected from the network. This simple action prevents them from generating false alarms and ensures that your monitoring system only tracks active devices. Regularly audit your network to identify and disable any unused or obsolete ports, and ensure that your configuration management process includes checks for unnecessary devices.
3. Clear Out Unnecessary Configurations
It’s important to periodically review your network’s configurations to remove redundant rules and obsolete settings. Doing so helps reduce complexity, ensuring that your monitoring tools only track relevant events. Consider:
- Cleaning up VLANs: If your network includes legacy or unused VLANs, remove them from your configuration.
- Reviewing SNMP settings: Only configure devices that need to be monitored. Avoid overloading your monitoring system with unnecessary checks or settings.
- Standardizing configuration templates: Create clear, standardized network configuration templates to ensure consistency and minimize errors.
4. Prioritize Actionable Alarms
Once unnecessary noise has been reduced, it’s crucial to focus your efforts on ensuring that actionable alarms are highlighted and managed effectively. Prioritize alerts that require immediate attention, such as those related to security breaches, hardware failures, or service outages. Using tools that allow you to categorize or tag alarms based on severity (critical, high, medium, low) can help your team triage alerts more efficiently.
The Benefits of Streamlined Network Monitoring
By reducing alarm fatigue, your team can spend more time addressing real problems and less time sifting through irrelevant alerts. The immediate benefits include:
- Improved response time to critical incidents, as alerts are more likely to be relevant and actionable.
- Enhanced productivity as engineers can focus on network optimization and troubleshooting, rather than getting bogged down in alarm noise.
- Better network reliability, with faster identification and resolution of actual issues.
Alarm fatigue is a significant challenge for network administrators, but it’s one that can be overcome. By tackling the root causes of alarm floods—flapping ports, unused devices, and excessive configuration clutter—you can streamline your network monitoring and ensure that your team’s attention is focused on what truly matters. With a clearer, more efficient monitoring system, you’ll not only reduce stress and improve productivity but also enhance the overall performance and security of your network.
Ready to eliminate the noise and focus on real problems? Start streamlining your network today and watch your team’s efficiency soar.

